II. The basic of nasal tip plasty 2: Cartilage graft
Most rhinoplasty for Asians is a surgery that heightens the dorsum and projeccts the nasal tip and a surgery while a bulbous and short nose is frequently as well. The alar cartilage of Asians is often small and weak compared with that of the Caucasians with disadvantages for nasal tip plastry. Since it is limited to change the shape of the nasal tip by simple suture alone, cartilage graft is necessary for the nasal tip plasty of most Asians.
The cartilage that is harvested from the nasal septum or ear is frequently used at the nasal tip plasty. In case of endonasal approach, the cartilage is inserted in the space provided in the nasal tip or tip onlay graft is conducted after exposing the alar cartilage and reinforcing the medial crus through columella strut graft.
Open rhinoplasty incision enables more effective suture and fixing of the cartilage and can bring variety of effects to the nasal tip byimplementing shield graft, cap graft, columellar strut graft, etc.
1) Shield graft
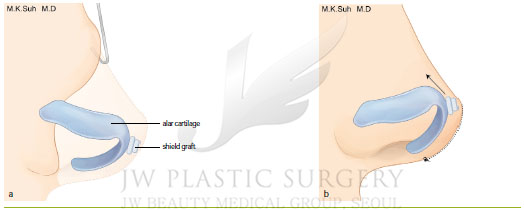
Shield graft is a shield-shaped graft at the front- and bottom-end of the nose tip. In other words, it is a graft placed throughout the middle crus and dome. It is effective in increasing nasal tip projection, enables a defined intratip lobule, and improves shape of the nasal tip by helping to lengthen the nose.
The cartilage harvested from ear or nasal septum is most frequently used and the width at the upper part is set to be about 6~8mm to display the tip defining point. The border area is made to be more inclined to display smooth curve after the surgery. In general, it is placed about 2~3mm is above the alar dome for better projection but in case of Koreans it is maximized. For those with thick skin and thin cartilage, the back of the grafted cartilage is reinforced by conducting additional cartilage graft to prevent tilting backward. By doing so, better result can be achieved.
2) On-lay graft
On-lay graft is one of the methods that can be easily used and indicates laying more than one layer of overlapped cartilage on the dome of the alar cartilage. To display tip defining point, the cartilage from the nasal septum or ear is used by laying a layer or several layers as high as desired in a width of 6~8mm. Since the ear cartilage is curved compared to that of the nasal septum, it is easy to create a smooth profile when laying on the dome.
The following should be considered during on-lay graft.
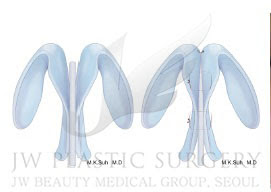
a. In case of a gap between the domes of the alar cartilage or weak lateral crus, the effect of projecting the nasal tip can be lost as the on-lay overlapped cartilage is stuck between the two domes. In such case, interdomal suture is conducted before performing on-lay graft.
b. In case of promoting on-lay graft in multiple layers, the medial crus of the alar cartilage must be strong enough to support the layers. Otherwise, the tip projecting effect may be lost as the weak medial crus is deviated by the force of the on-lay graft . Therefore in case of very weak medial crus, it should be firmly supported with columellar strut graft for maximal projection.
thin skin layer, the cartilage can be weakened or the cartilage graft can be covered with the fascia or
AlloDerm.
3) Columellar strut graft
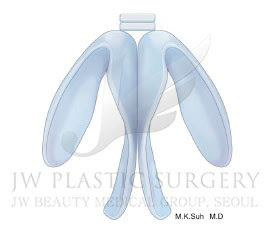
Columellar strut graft is one of the most frequently used basic surgical methods to project the nasal tip. The cartilage to be grafted is inserted between the medial crura of the alar catilages in shape of a column, and it should be fixed without protrusion above or anterior to the crus. As for materials for the strut, nasal septal cartilage which is thin, straight shaped, and easy to harvest is most frequently used; however, the ear, costal, or allogenous costal cartilage can be used as an alternative for patients with limited the nasal septum.
Principles for projecting the nasal tip with the columellar strut graft are as follows.
a. The nasal tip can be projected by promoting interdomal suture, transdomal suture, or medialization of the lateral crus at the upper part around the strut tip after inserting the strut. Also, it is possible to sustain and
support the force and weight of the onlay graft. In other words, it works to reinforce the effect of various
suture techniques that project the nasal tip or onlay graft.
b. It prevents tip height loss caused by the deviated meidal crus as the strut reinforces the medial crus.
c. It prevents lowering of the nasal tip as the tip is pulled downward when smiling.
Columellar strut is classified into fixed type that contacts the ANS and floating type that is separated from the ANS. The floating type is recommended as cushion effect is preserved when pressing the nasal tip.
Therefore, it is smooth when touching the nasal tip and presents natural nose tip when smiling. Although the strut doesn’t directly contact ANS, the effect of the nose tip support and projection is relatively good, and such columellar strut graft works as firm support along with shield graft or cap graft to obtain more projected nasal tip.
When requiring much stronger projection of the nasal tip, a long column in contact with the ANS is used (Fixed type). In this case, the nasal tip gets hard after the surgery and the shape of the tip becomes fixed when smiling causing an artificial shape.
|
|